A Homeowner’s Guide to Sheds and Greenhouses for Landscaping Projects
Sheds and greenhouses are practical additions to any backyard, providing storage, workspace, and protection for plants. Whether you're looking to store gardening tools, create a space for hobbies, or extend your growing season, a well-designed Shed or Greenhouse can be both functional and aesthetically pleasing. This guide will explore the types of sheds and greenhouses, their uses, materials, and key considerations for installation and maintenance to help you make the best choice for your home and garden.
Types of Sheds
1. Storage Sheds
Storage sheds are designed primarily for housing tools, equipment, and outdoor gear. They come in various sizes and styles, providing a dedicated space to keep your yard organized and clutter-free.
Key Features:
Size Variety: Available in sizes ranging from small, compact units to large structures with additional space for workshops or hobbies.
Lockable Doors: Secure entry with options for Padlocks or built-in locks, ensuring your items are safe from theft and weather damage.
Ventilation: Often include vents or windows to prevent moisture buildup and provide airflow.
Uses:
Ideal for storing lawnmowers, garden tools, bicycles, and outdoor equipment.
Can double as a small workshop for DIY projects, potting plants, or other hobbies.
Benefits:
Keeps outdoor spaces tidy by providing a dedicated storage area.
Protects tools and equipment from the elements, extending their lifespan.
Customizable to match the aesthetic of your yard or home.
Considerations:
Choose a shed size based on your storage needs, ensuring it doesn’t overwhelm your yard. Ventilation is important to prevent condensation, especially if you’re storing tools that could rust or materials that need to stay dry.
2. Workshop Sheds
Workshop sheds are larger structures that provide ample space for DIY projects, woodworking, gardening, or other hobbies. These sheds often include built-in workbenches, shelving, and electrical outlets for powering tools.
Key Features:
Workspace: Offers enough room for projects and storage of tools and materials.
Electrical Access: Many workshop sheds can be wired for electricity to power tools, lighting, and other equipment.
Custom Interiors: Can be outfitted with shelving, pegboards, and workbenches to create a functional workspace.
Uses:
Best for homeowners looking to create a space for woodworking, gardening, or other hands-on activities.
Suitable for larger equipment and tool storage.
Benefits:
Provides a dedicated space for hobbies and projects, keeping the garage or basement free from clutter.
Customizable to suit specific needs, such as additional storage, electrical outlets, or workbenches.
Considerations:
Workshop sheds require more space and often need permits for electricity and larger footprints. Plan ahead to ensure there’s enough room for both storage and workspace without crowding your yard.
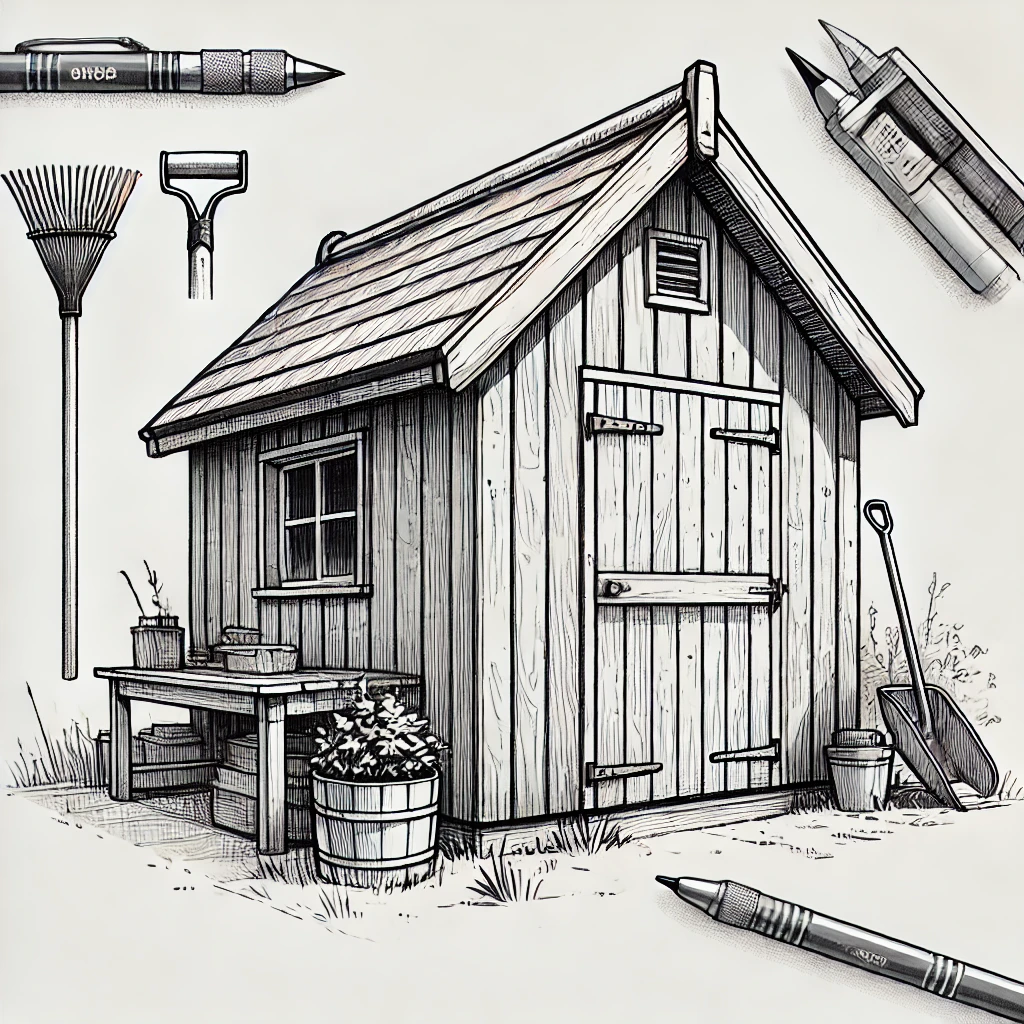

3. Garden Sheds
Garden sheds are designed with avid gardeners in mind. They offer space for storing garden tools, potting plants, and organizing gardening supplies, often with windows and shelving to create a functional gardening hub.
Key Features:
Shelving and Storage: Includes racks, hooks, and shelves for organizing tools, seeds, pots, and soil.
Potting Bench: Many garden sheds feature a dedicated potting area for planting and repotting.
Windows: Natural light through windows makes gardening tasks easier and helps with Seed Starting.
Uses:
Ideal for storing gardening tools, fertilizers, pots, and seeds.
Provides a workspace for potting, Pruning, and tending to plants.
Benefits:
Offers a central location for all gardening tasks and supplies.
Keeps tools organized and easily accessible.
Protects delicate materials like seeds and potting soil from weather damage.
Considerations:
Ensure the shed has adequate ventilation and sunlight for tasks like seed starting or potting. It’s important to select materials that can withstand moisture, especially if plants are being tended to inside the shed.
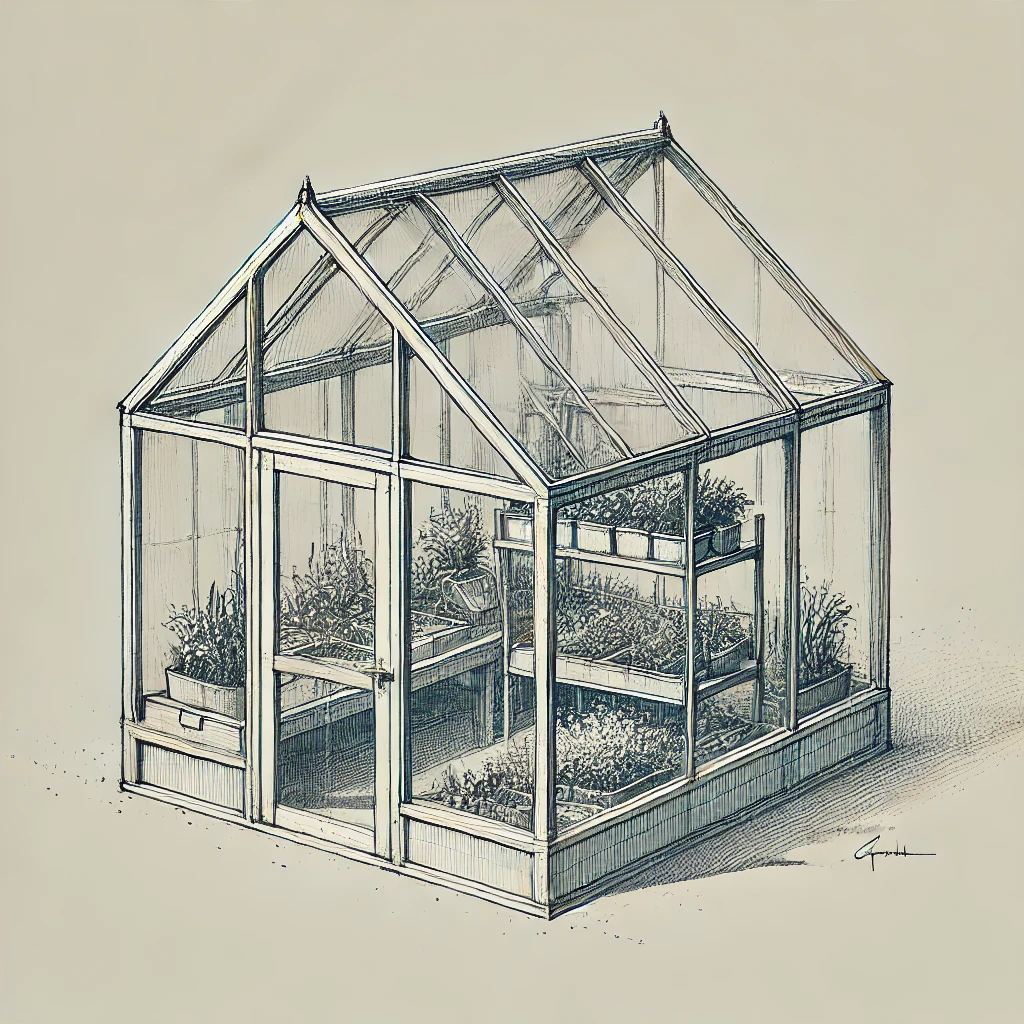

Types of Greenhouses
1. Freestanding Greenhouses
Freestanding greenhouses are independent structures designed to grow plants year-round by providing a controlled environment. These greenhouses are ideal for serious gardeners looking to extend their growing season.
Key Features:
Ventilation and Climate Control: Equipped with vents, fans, or heaters to regulate temperature and humidity.
Natural Light: Built with transparent materials like glass or polycarbonate that allow maximum sunlight.
Space for Growing: Includes shelving, benches, and growing racks to accommodate multiple plants.
Uses:
Best for growing plants, vegetables, and flowers throughout the year, regardless of weather.
Suitable for starting seeds, propagating plants, or growing tropical and delicate species.
Benefits:
Extends the growing season, allowing for year-round gardening.
Protects plants from extreme temperatures, pests, and weather.
Customizable with heating and cooling systems for optimal plant growth.
Considerations:
Freestanding greenhouses require adequate space and can be a significant investment. Maintenance is key, especially with ventilation and temperature control, to prevent mold, mildew, or overheating.
2. Lean-To Greenhouses
Lean-to greenhouses are attached to an existing building, such as a home or garage. They are a space-saving option for homeowners who want a greenhouse but have limited yard space.
Key Features:
Attached Structure: Built against a wall of an existing building, sharing one or more walls.
Space-Saving: Takes up less room than a freestanding greenhouse.
Access to Utilities: Easier to connect to heating, water, or electricity from the main building.
Uses:
Perfect for growing herbs, vegetables, or small plants in a limited space.
Can be used to extend the growing season for specific plants close to the home.
Benefits:
Requires less space than freestanding greenhouses.
Easier to install heating and lighting systems using the home's existing infrastructure.
Provides convenient access for everyday gardening tasks.
Considerations:
Lean-to greenhouses rely on the building they’re attached to for support and stability. Consider the orientation and amount of sunlight the structure will receive based on its location.
3. Cold Frames and Mini Greenhouses
Cold frames and mini greenhouses are smaller, portable structures that provide a simple way to protect plants from frost and extend the growing season.
Key Features:
Compact Size: Small and often portable, making them ideal for patios, decks, or small gardens.
Simple Design: Typically made from a transparent cover over a wooden or plastic frame.
Affordable: Less expensive and easier to set up than traditional greenhouses.
Uses:
Ideal for starting seeds or protecting delicate plants during cold weather.
Suitable for small-scale gardening in limited spaces.
Benefits:
Affordable and easy to set up.
Helps protect plants from frost, cold, and wind.
Portable and easy to move as needed.
Considerations:
Cold frames and mini greenhouses provide limited space and climate control compared to larger structures. They are best suited for small gardens or specific tasks like seed starting.
Materials for Sheds and Greenhouses
1. Wood
Wood is a popular choice for both sheds and greenhouses due to its natural appearance and durability. However, wood requires regular maintenance to prevent rot, warping, and insect damage.
2. Metal
Metal sheds offer durability and security, but they may become hot in direct sunlight and are prone to rust if not properly treated. Metal frames are also commonly used for greenhouses because of their strength.

3. Plastic and Resin
Plastic and resin are lightweight, affordable, and low-maintenance materials used for sheds and greenhouses. They resist rot and rust, making them ideal for humid environments, but they may not offer the same durability as wood or metal. For example, Rubbermaid has an expansive line of plastic sheds for homeowners.
4. Glass and Polycarbonate
For greenhouses, glass and polycarbonate are popular materials due to their transparency and ability to let in light. Glass offers clarity but is heavy and expensive, while polycarbonate is lightweight and more durable, though it may scratch over time.
Installation Considerations
1. Permits and Regulations
Before building a shed or greenhouse, check local zoning laws and homeowner association (HOA) regulations to ensure compliance. Some areas may require permits for larger structures.
2. Location
Choose a location that receives adequate sunlight for greenhouses or is easily accessible for sheds. Consider proximity to the house, available space, and drainage needs.
3. Foundation
A solid foundation is essential for both sheds and greenhouses. Options include Concrete slabs, Gravel bases, or Pressure-Treated Wood platforms to ensure stability and prevent water damage.

Maintenance Tips
1. Cleaning and Inspections
Regularly clean the exterior of your shed or greenhouse to prevent dirt, mold, and Algae buildup. Inspect for any damage, such as leaks, rust, or rot, and address issues promptly to prevent further deterioration.
2. Temperature Control
For greenhouses, monitor temperature and humidity levels to prevent overheating or moisture issues. Install fans, vents, or heaters as needed to maintain a stable growing environment.
3. Pest Prevention
Keep sheds and greenhouses pest-free by sealing any gaps or cracks where insects or rodents may enter. Use natural pest control methods in greenhouses to protect plants without harmful chemicals.
Further Reading
Wrap-Up
Sheds and greenhouses are versatile additions to any backyard, providing valuable storage, workspace, and a controlled environment for growing plants. Whether you need a Storage Shed for tools, a greenhouse to extend your growing season, or a custom-built workshop for hobbies, choosing the right structure can enhance the functionality and appeal of your outdoor space.
Consider factors like the size, materials, location, and local regulations when planning your shed or greenhouse project. With proper installation and maintenance, these structures will not only improve the aesthetics of your garden but also offer long-lasting practicality. Whether you’re an avid gardener or a DIY enthusiast, a well-designed shed or greenhouse is a valuable investment in your home’s landscape.