A Comprehensive Guide to Steel and Aluminum Building Materials for Homeowners

When embarking on a major construction project or rebuild, selecting the right materials is key to ensuring durability, strength, and longevity. Steel and aluminum are two widely used building materials in both residential and commercial construction. Known for their strength, versatility, and resistance to the elements, these metals can be used in everything from structural Framing to roofing and Siding.
This guide provides an overview of the various types of steel and aluminum materials available for homeowners, their uses, and key considerations for integrating them into your construction project.
Steel Building Materials
Steel is a robust and versatile material widely used in construction for its strength, durability, and ability to withstand harsh conditions. There are different types of steel used in residential construction, each with its own specific application.
1. Structural Steel
Structural steel is used in the framework of buildings, providing the essential skeleton that supports walls, floors, and roofs.
Use: Primarily used for load-bearing beams, columns, and trusses in modern residential and commercial buildings.
Common Types:
I-Beams (W-Beams): Shaped like the letter "I" or "H," I-beams are used in structural framing, especially for floor Joists and support beams.
Steel Channels: Used for lighter structural framing or as Bracing.
Steel Tubes and Pipes: Often used in smaller structural applications or as part of railing systems and staircases.
Advantages: High strength-to-weight ratio, resistant to fire, and able to support large spans, reducing the need for interior load-bearing walls.
Disadvantages: Requires special tools and skills for installation, and may be prone to corrosion if not properly treated or coated.
2. Cold-Formed Steel
Cold-formed steel is used for non-structural applications such as interior framing or Cladding.
Use: Ideal for interior wall studs, roofing, and floor framing.
Advantages: Lightweight, easier to transport, and resistant to Termites, rot, and Mold. It also provides better dimensional stability than wood.
Disadvantages: Not as strong as structural steel, and additional Insulation may be needed for Energy Efficiency.
3. Galvanized Steel
Galvanized steel is coated with a layer of zinc to protect it from rust and corrosion, making it ideal for outdoor applications or areas exposed to moisture.
Use: Commonly used for roofing, gutters, and exterior panels.
Advantages: Corrosion-resistant and durable, making it suitable for roofing and other outdoor structures exposed to the elements.
Disadvantages: More expensive than untreated steel, and the zinc coating can wear off over time.
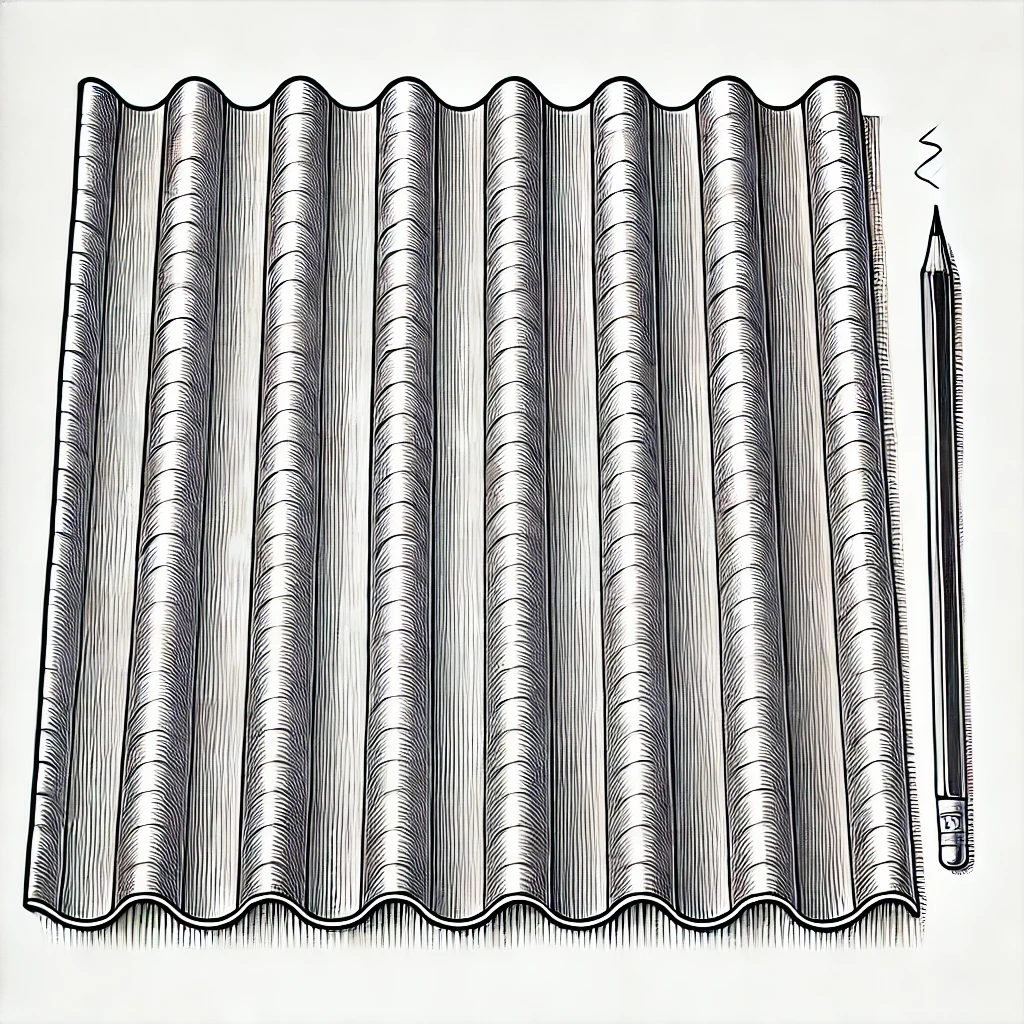

4. Corrugated Steel Panels
Corrugated steel panels are commonly used for roofing and siding, providing a durable and weather-resistant finish.
Use: Often used for Metal Roofing and siding in modern or industrial-style homes.
Advantages: Lightweight yet strong, corrugated steel is easy to install, durable, and resistant to wind, rain, and snow.
Disadvantages: May require additional insulation to prevent heat and cold transfer, and can be noisy during rainstorms if not properly insulated.
5. Steel Rebar
Steel Reinforcement bars (rebar) are used to reinforce Concrete, adding Tensile Strength to materials that are otherwise weak in tension.
Use: Essential in foundations, slabs, and other concrete structures.
Advantages: Increases the strength and durability of concrete structures, reducing the risk of cracking or shifting over time.
Disadvantages: Requires precision in placement and can corrode over time if exposed to moisture without proper protection.
Aluminum Building Materials
Aluminum is another popular building material, particularly valued for its lightweight properties, Corrosion Resistance, and ease of maintenance. Although not as strong as steel, aluminum is often used for applications where weight and weather resistance are important considerations.
1. Aluminum Siding
Aluminum siding is used as an exterior cladding material in residential buildings. It is lightweight, durable, and requires minimal maintenance.
Use: Common for home exteriors, especially in areas prone to extreme weather, such as coastal or humid regions.
Advantages: Resistant to rust and corrosion, does not crack or warp, and is fire-resistant. Aluminum siding can also be painted to match any design.
Disadvantages: More expensive than Vinyl Siding, and can dent or scratch more easily.
2. Aluminum Roofing
Aluminum roofing is becoming increasingly popular due to its durability and resistance to corrosion. It is commonly used for both residential and commercial buildings.
Use: Used as a long-lasting alternative to traditional roofing materials like Asphalt Shingles.
Advantages: Extremely durable, lightweight, and resistant to rust and corrosion. Aluminum roofing reflects heat, making it energy-efficient for homes in hot climates.
Disadvantages: Can be more expensive than steel or Asphalt roofing, and requires proper insulation to reduce noise from rain or hail.
3. Aluminum Framing
Aluminum framing is used in windows, doors, and curtain walls, offering a sleek and modern aesthetic while being lightweight and corrosion-resistant.
Use: Often used for window and door frames, as well as structural glazing in modern homes.
Advantages: Lightweight, resistant to rust, and easy to maintain. Aluminum can also be thermally broken to improve energy efficiency.
Disadvantages: Not as strong as steel, and may require reinforcement for large spans.
4. Aluminum Composite Panels (ACP)
Aluminum composite panels are composed of two thin sheets of aluminum bonded to a non-aluminum core, often used for cladding, insulation, or aesthetic purposes.
Use: Ideal for modern exteriors, insulation cladding, and decorative façades.
Advantages: Lightweight, durable, and available in a variety of colors and finishes. Aluminum composite panels offer good Thermal Insulation and resistance to weather.
Disadvantages: More expensive than traditional siding materials, and the non-aluminum core may need to meet fire safety standards depending on the application.
5. Aluminum Gutters
Aluminum is a popular choice for gutters due to its lightweight nature and resistance to corrosion.
Use: Gutters and downspouts in residential and commercial buildings.
Advantages: Rust-resistant, lightweight, and available in a wide range of colors and finishes. Aluminum gutters are relatively inexpensive and easy to install.
Disadvantages: Can dent more easily than steel, and may need to be replaced more frequently in areas with heavy snowfall or hail.
Typical Sizes of Steel and Aluminum Building Materials
Steel Sizes:
I-Beams: Depths range from 4 inches to over 12 inches, depending on load requirements.
Steel Channels: Available in depths from 1 to 4 inches, with varying flange widths.
Cold-Formed Steel Studs: Common stud sizes include 2x4 inches and 2x6 inches, similar to wood framing.
Rebar: Sizes range from #3 (⅜ inch diameter) to #18 (2 ¼ inch diameter) for large structural applications.
Aluminum Sizes:
Aluminum Siding: Panels typically come in widths of 6 to 12 inches, with lengths up to 12 feet.
Aluminum Roofing Sheets: Common sizes range from 2 to 3 feet wide and up to 12 feet long.
Aluminum Composite Panels: Standard thicknesses are 3mm, 4mm, and 6mm, with dimensions ranging from 4x8 feet to 5x10 feet.
Aluminum Gutters: Standard Gutter widths are 5 inches for residential applications, and 6 inches for larger or commercial buildings.
Further Reading
For more detailed information on steel and aluminum building materials and their applications, consider the following resources:
American Institute of Steel Construction (AISC) – A comprehensive resource for steel construction standards, practices, and benefits.
Steel Construction Institute – A detailed guide to steel construction, design, and applications.
Metal Roofing Alliance – Information on aluminum and steel roofing, including cost comparisons and installation guides.
The Aluminum Association – A resource for aluminum construction materials and their benefits in residential and commercial building.
Wrap-Up
Steel and aluminum are indispensable materials in modern construction, offering a balance of strength, durability, and aesthetic versatility. Steel is favored for structural applications due to its high load-bearing capacity, while aluminum is preferred for lightweight, corrosion-resistant features like roofing, siding, and window framing. Both materials offer excellent durability and can withstand harsh environmental conditions, making them ideal for long-term construction projects.
Choosing the right material for your construction project depends on several factors, including load requirements, weather conditions, aesthetic preferences, and budget. By understanding the properties and uses of steel and aluminum, homeowners can make informed decisions that ensure the success of their project while enhancing the overall value of their home.
For further exploration, check out the additional reading resources to dive deeper into the technical aspects of steel and aluminum construction and discover how to best incorporate these materials into your rebuild.