Hardening Roofs & Gutters with Wildfires in Mind

Your roof and Gutter system are highly susceptible to damage from wildfires. Embers carried by wind can land on your roof or in your gutters, igniting debris and potentially setting your home ablaze. Harden your roof and gutters to withstand wildfire threats by choosing fire-resistant materials, keeping them clean, and implementing protective barriers.
This article details effective strategies to reinforce your roof and gutters, enhancing their ability to resist ignition from flying embers and radiant heat.

Fire-Resistant Roofing Materials
Choosing the right roofing material is one of the most critical steps in hardening your home against wildfires. Roofs are classified by their fire resistance, with Class A being the highest level of protection.
Class A Fire-Rated Materials: Install a Class A fire-rated roof for the best protection. Materials with this rating are highly resistant to fire and can prevent flames from spreading. Examples include:
Asphalt Shingles: Look for Fiberglass-based Asphalt shingles, which are typically more fire-resistant than organic-based varieties.
Metal Roofing: Metal roofing is non-combustible, durable, and can withstand high temperatures, making it an excellent choice for wildfire-prone areas.
Clay and Concrete Tiles: These heavy, non-combustible tiles offer significant fire resistance and don’t ignite easily, though they may require additional structural support.
Slate: Slate Roofing is naturally fire-resistant and very durable, but it can be heavy and may also need additional support.
Roofing Systems with Multiple Layers: Some roofing systems combine several layers to create a barrier against fire. For example, installing a fire-resistant underlayment below your shingles can enhance the overall protection.
Ember-Resistant Vents and Eaves
Vents and eaves allow air to circulate through your attic, but they can also let embers in. Ember-resistant venting and eave design are crucial to reducing your roof’s vulnerability to wildfires.
Ember-Resistant Vents: Install vents with ember-resistant mesh, typically with openings no larger than 1/8 inch. These vents prevent embers from entering while still allowing for proper Ventilation. Look for models specifically designed and rated for wildfire resistance.
Boxed or Closed Eaves: Eaves with exposed rafters can easily catch embers. Opt for boxed or closed eaves, which are more resistant to ember intrusion. They help protect your roof by limiting places where embers can lodge.
Fire-Blocking Materials: When installing soffits and eaves, choose fire-resistant materials like fiber Cement or metal. Adding an under-eave Vent cover can provide an additional layer of defense against embers.
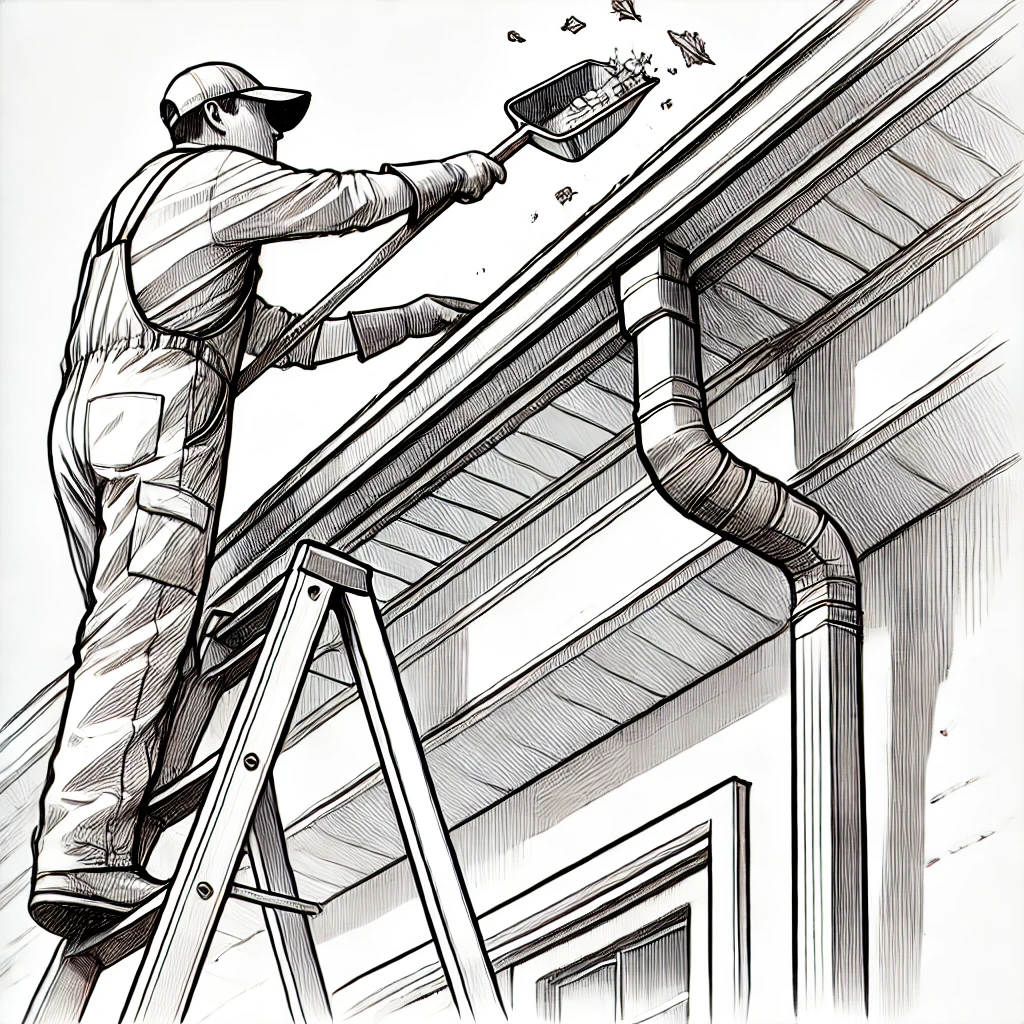

Maintaining a Clear Roof and Gutter System
Embers are more likely to ignite dry leaves, pine needles, and other debris, which makes regular maintenance of your roof and gutters essential.
Regular Cleaning: Routinely clean your roof and gutters, especially during fire season, to remove any buildup of leaves, pine needles, or other Flammable debris. This reduces potential fuel sources where embers might land.
Install Gutter Guards: Gutter guards can prevent debris from accumulating, making it easier to maintain a clear gutter system. Opt for metal gutter guards rather than plastic, as metal is non-combustible and more resistant to heat.
Downspout Extensions: Downspout extensions help direct water away from the base of your home, but they can also prevent dry debris from settling in tight corners of your roof or gutter system. This minimizes potential ignition points around your roofline.
Using Fire-Resistant Roof Seals and Coatings
Additional fire-resistant treatments can protect roofing materials by creating a barrier between embers and combustible surfaces.
Fire-Retardant Sprays: Some fire-retardant sprays can be applied to existing roofing materials to increase fire resistance. These sprays may need to be reapplied periodically, so consult the product Specifications for proper maintenance.
Heat-Resistant Coatings: Special heat-resistant coatings can protect certain types of roofing materials, such as wood shakes, by reducing their flammability. Ensure any coating or Sealant you use is approved for wildfire protection and follows local fire safety regulations.
Sealing Vulnerable Areas: Pay special attention to areas where the roof meets the walls or where there are transitions between different roofing materials. Use fire-resistant Caulk or sealants in these areas to reduce the risk of embers entering or igniting materials.
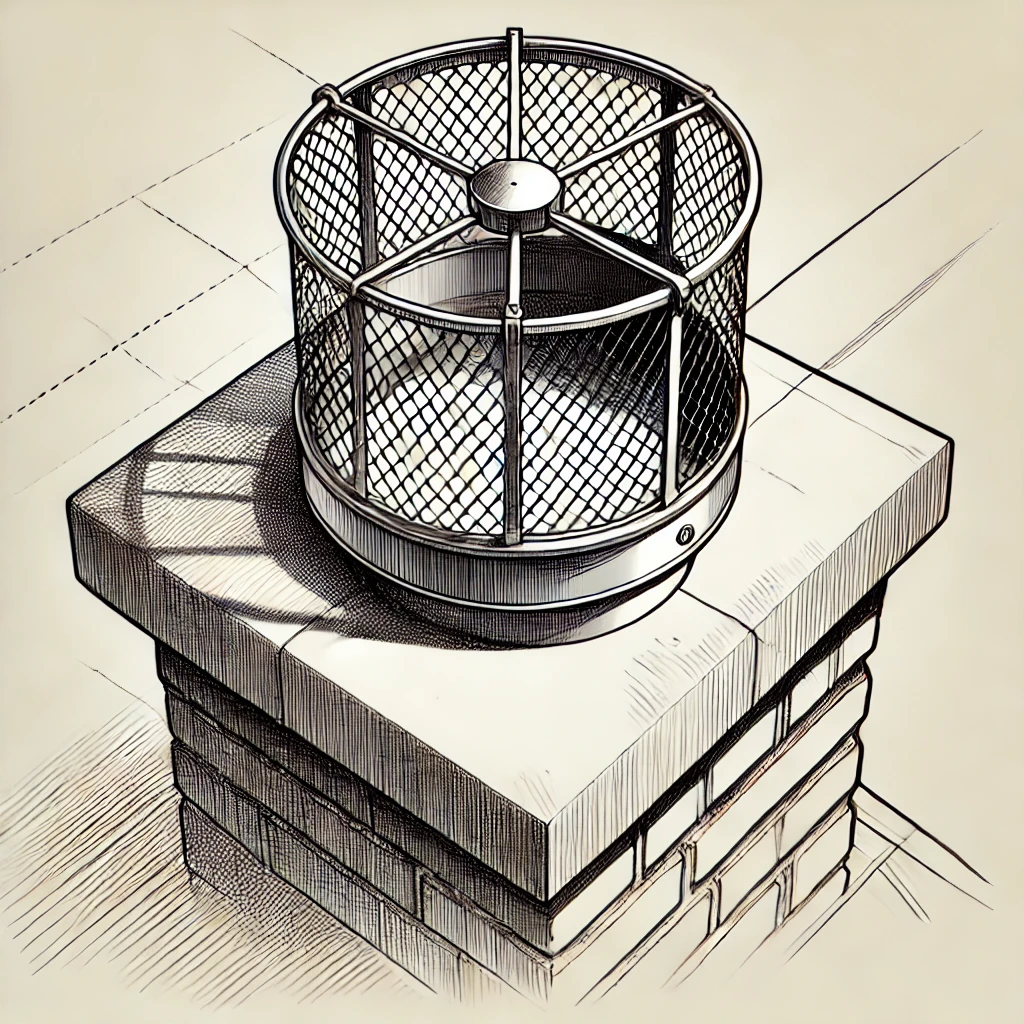
Installing Spark Arresters on Chimneys
If your roof has a Chimney, it’s crucial to prevent embers from escaping through it or entering from above. Spark arresters are designed to trap embers and prevent them from spreading.
Spark Arrester Requirements: Install a spark arrester with openings no larger than ½ inch on your chimney. This helps keep embers contained and reduces the likelihood of nearby vegetation or debris igniting.
Non-Combustible Chimney Caps: Choose a Chimney Cap made of non-combustible materials, such as metal, to prevent embers from landing on the roof or in nearby gutters. Ensure the cap is securely attached and regularly inspected for any signs of damage.
Vegetation Management Around the Roofline
Proper vegetation management near your roof can prevent overhanging branches or climbing plants from catching fire and spreading flames to your roof.
Trim Back Overhanging Branches: Trim tree branches so they are at least 10 feet away from the roof. Overhanging branches can drop leaves and twigs onto the roof, increasing the amount of combustible material present.
Remove Vines and Climbing Plants: Vines and climbing plants can easily catch fire and provide a direct path to your roof. Remove any plants that climb the walls or eaves, especially those that extend onto the roof surface.
Maintain a Fire-Resistant Landscape: In addition to managing nearby vegetation, use fire-resistant plants around the home to create a defensible space. This helps prevent flames from getting close enough to ignite the roof.
Additional Resources
Hardening your roof and gutters to withstand wildfires is essential for creating a fire-resistant home. For more guidance and resources, consult the following:
National Fire Protection Association (NFPA): NFPA provides guidelines and resources for fire-resistant building materials and home hardening practices. Visit NFPA’s Firewise USA Program to learn more about wildfire preparedness.
Ready, Set, Go! Program: This program, developed by the International Association of Fire Chiefs, offers information on preparing your home for wildfire season. Check out their resources at Ready, Set, Go! for tips on home hardening and evacuation planning.
CalFire: The California Department of Forestry and Fire Protection has live maps to track wildfires and advice on prevention measures. Highly recommended resource: https://www.fire.ca.gov/
Wrap-Up
By hardening your roof and gutters, you’re taking proactive steps to defend your home from wildfires. From choosing fire-resistant roofing materials to managing embers with regular maintenance, each measure reduces the chance of ignition and helps protect your home from damage.
Combining these strategies with defensible space around your property enhances your home’s resilience, providing greater peace of mind during wildfire season. Through thoughtful preparation, you can create a safer, more fire-resistant home environment for you and your loved ones.