Maintaining Your Home's Attic

Your attic plays a vital role in your home’s Energy Efficiency, Ventilation, and overall structural integrity. Regular maintenance of your attic helps prevent moisture buildup, Pest infestations, Insulation degradation, and damage to your roof and Framing. By keeping your attic well-maintained, you can improve indoor air quality, lower energy costs, and extend the lifespan of your home’s roof and insulation.
This article provides a comprehensive guide to maintaining your attic, focusing on ventilation, insulation, moisture control, and pest prevention.
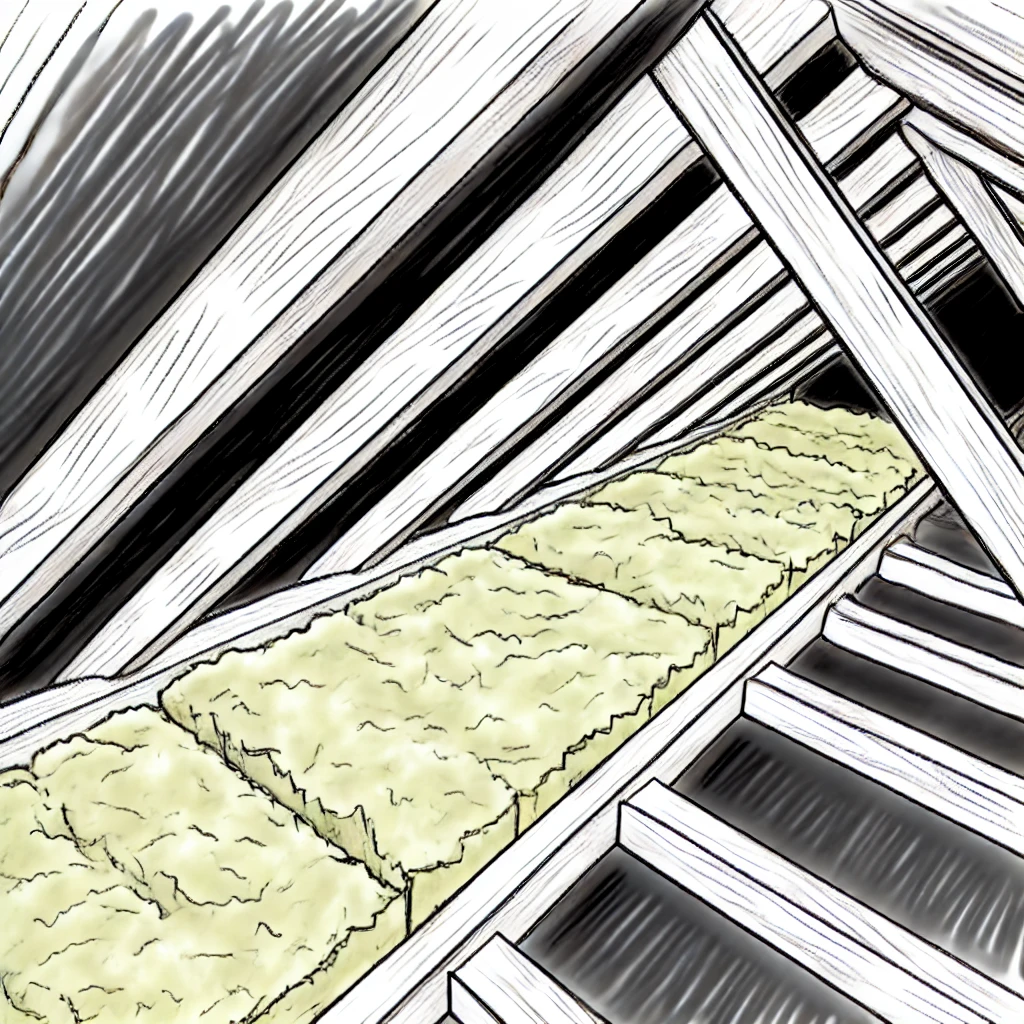
Inspecting Insulation
Proper insulation in your attic is key to maintaining comfortable indoor temperatures and reducing energy costs. Over time, insulation can degrade or become less effective due to moisture, pests, or improper installation.
Check Insulation Levels: Inspect your attic insulation to ensure it’s sufficient for your climate. Insulation should be thick enough to cover the floor Joists. In colder climates, the recommended insulation level is typically between R-38 and R-60, while milder climates may require lower levels. If the insulation looks compressed, uneven, or insufficient, consider adding more.
Look for Signs of Moisture: Moisture can degrade insulation, making it less effective. Inspect insulation for signs of Mold, mildew, or dampness. If you notice wet spots or musty odors, address the source of the moisture (such as a roof leak or poor ventilation) before replacing any damaged insulation.
Avoid Blocking Vents: When adding insulation, make sure it doesn’t block Soffit vents or other ventilation pathways. Blocking vents can reduce airflow and lead to moisture buildup, which can damage insulation and other attic components.
Choose the Right Insulation Material: The most common types of attic insulation are Fiberglass batts, blown-in cellulose, and spray foam. If you’re unsure which type is best for your home, consult a professional to assess your needs and recommend the appropriate material for your climate and energy goals.
Ensuring Proper Ventilation
Good attic ventilation prevents excess heat and moisture from building up, which can cause roof damage, mold growth, and higher energy bills. A well-ventilated attic stays cool in summer and prevents condensation in winter.
Check Vent Openings: Your attic should have sufficient intake and exhaust vents, such as soffit vents, Ridge vents, Gable vents, or attic fans, to promote proper airflow. Inspect these vents regularly to ensure they’re free of obstructions like debris, insulation, or nests.
Ensure Balanced Airflow: Attic ventilation works best when there’s a balance between intake (air coming in) and exhaust (air going out). Intake vents, typically located in the soffits, allow cool air to enter the attic, while exhaust vents, such as ridge or roof vents, allow warm air to escape. This balance prevents heat and moisture buildup, protecting your attic and roof.
Consider Installing Attic Fans: In warmer climates, attic fans can help reduce attic temperatures by expelling hot air more efficiently. Solar-powered attic fans are an energy-efficient option, as they run on sunlight and don’t increase your electricity usage.
Look for Signs of Poor Ventilation: If your attic feels excessively hot in summer, has visible condensation on surfaces, or has ice dams forming on the roof during winter, these could be signs of poor ventilation. Address these issues promptly to prevent long-term damage to your roof and attic structure.
Controlling Moisture and Preventing Mold
Moisture control is one of the most critical aspects of attic maintenance. High humidity and condensation in the attic can lead to mold growth, wood rot, and damage to insulation and structural components.
Check for Roof Leaks: Periodically inspect the attic for signs of roof leaks, such as water stains, damp insulation, or wet spots on the Ceiling. Look closely around roof penetrations, such as chimneys, vents, and skylights, where leaks are most likely to occur. Address leaks as soon as they’re discovered to prevent further damage.
Prevent Condensation: In colder climates, warm air from the living spaces below can rise into the attic and condense on cold surfaces, leading to moisture buildup. Ensure that your attic is properly insulated to prevent heat transfer and seal any gaps or openings where warm air might escape from below.
Inspect Flashing and Sealants: Flashing around chimneys, vents, and other roof penetrations should be intact and in good condition. Cracked or damaged flashing can allow water to seep into the attic. If you notice any gaps or deterioration in flashing or sealants, have them repaired or replaced to prevent leaks.
Install Vapor Barriers: Vapor barriers, often made of plastic sheeting or specialized paints, can help prevent moisture from entering your attic. Install a Vapor Barrier under the attic insulation to reduce the amount of moisture rising from your home’s living areas into the attic space.

Pest Control and Prevention
Attics are attractive spaces for pests like rodents, insects, and birds, which can cause damage to insulation, wiring, and structural components. Preventing pests from entering your attic is crucial for maintaining a clean and safe space.
Seal Entry Points: Inspect your attic for any openings, such as gaps around vents, chimneys, or roof edges, that could allow pests to enter. Use Caulk, Steel wool, or other appropriate materials to seal gaps and prevent pests from gaining access.
Look for Signs of Pests: Regularly check for signs of pest activity, such as droppings, nests, gnaw marks, or damaged insulation. Rodents can chew through electrical wiring, creating fire hazards, while insects can infest wood and insulation. If you notice signs of an Infestation, contact a pest control professional to address the problem.
Remove Attractants: Make sure food, garbage, and pet food are properly stored to avoid attracting pests to your home. Keep tree branches trimmed away from your roof to reduce the likelihood of animals like squirrels or raccoons gaining access to your attic.
Maintaining Structural Integrity
The structural components of your attic, including beams, rafters, and the roof deck, need to be in good condition to support your roof and protect your home.
Inspect Beams and Rafters: Check the beams and rafters in your attic for any signs of damage, such as cracks, splits, or sagging. Wood rot, mold, or insect infestations can weaken these components, putting your roof’s structural integrity at risk. If you notice damage, consult a professional to assess the extent and determine necessary repairs.
Look for Signs of Sagging or Bowing: If you notice that parts of your roof or attic ceiling are sagging or bowing, it could be a sign of a weakened roof structure or improper load distribution. This is particularly common in older homes or homes that have experienced heavy snowfall or water damage. Address any structural concerns promptly to prevent further damage.
Inspect the Roof Decking: The roof decking, or the layer of wood that supports your roof, should be free of rot, mold, or warping. If you notice soft spots or areas of discoloration, it could be a sign of water damage from a roof leak. Repair any damaged decking to maintain the stability of your roof and prevent further deterioration.
Energy Efficiency and Temperature Control
A well-maintained attic helps regulate your home’s temperature, reducing heating and cooling costs. Improving the energy efficiency of your attic can also make your home more comfortable year-round.
Install Radiant Barriers: Radiant barriers are reflective materials installed on the underside of the roof that help reduce heat gain in the summer. These barriers can lower attic temperatures and reduce the strain on your air conditioning system, particularly in warmer climates.
Check for Air Leaks: Air leaks between your attic and living space can allow conditioned air to escape, making your HVAC system work harder. Check for and seal gaps around Plumbing vents, chimneys, and attic hatches to improve your home’s energy efficiency.
Monitor Attic Temperatures: Attic temperatures can fluctuate significantly with outdoor conditions. Installing a temperature monitor in your attic allows you to track temperature changes and identify potential ventilation or insulation issues that may need to be addressed.
Additional Resources
For more information on attic maintenance and energy efficiency, explore these resources:
Energy.gov: The U.S. Department of Energy offers detailed guidance on attic insulation and ventilation for improving energy efficiency. Visit Energy Saver for tips and recommendations.
National Roofing Contractors Association (NRCA): NRCA provides advice on roof maintenance, attic ventilation, and insulation. Visit NRCA for more information on keeping your attic and roof in top condition.
Wrap-Up
Maintaining your attic is essential for protecting your home from moisture, pests, and structural damage while improving energy efficiency. By regularly inspecting insulation, ensuring proper ventilation, controlling moisture, and preventing pest infestations, you can keep your attic in excellent condition.
Additionally, addressing any structural concerns promptly and enhancing energy efficiency with proper insulation and sealing will ensure your attic continues to support the comfort and longevity of your home. With consistent upkeep, your attic will remain a functional, well-maintained space that contributes to the overall health of your house.